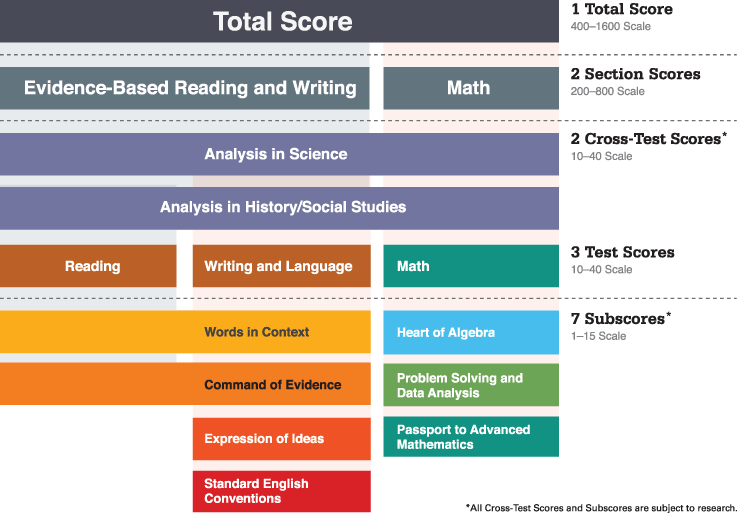
The SAT Reasoning Test (formerly Scholastic Aptitude Test and Scholastic Assessment Test, pronounced as three separate letters) is a standardized test for college admissions in the United States. The SAT is owned, published, and developed by the College Board, a not-for-profit organization in the United States. It was formerly developed, published, and scored by the Educational Testing Service which still administers the exam. The test is intended to assess a student’s readiness for college. It was first introduced in 1901, and its name and scoring have changed several times. The current SAT Reasoning Test, introduced in 2005, takes three hours and forty-five minutes, and costs $47 ($75 International), excluding late fees. Possible scores range from 600 to 2400, combining test results from three 800-point sections (Mathematics, Critical Reading, and Writing).
The College Board states that the SAT measures literacy and writing skills that are needed for academic success in college. They state that the SAT assesses how well the test takers analyze and solve problems—skills they learned in school that they will need in college. The SAT is typically taken by high school sophomores, juniors and seniors. Specifically, the College Board states that use of the SAT in combination with high school grade point average (GPA) provides a better indicator of success in college than high school grades alone, as measured by college freshman GPA. Various studies conducted over the lifetime of the SAT show a statistically significant increase in correlation of high school grades and freshman grades when the SAT is factored in.